Supply Chain Risk & Resilience Assessment
A Consulting-Style Analysis of Patagonia’s Black Hole® Pack
Case Study Overview
Patagonia’s sustainability-first sourcing model makes it an ideal case for examining how ethical and environmental constraints interact with supply chain risk and resilience.
This project provides an executive-style assessment of concentration, logistics exposure, and operational trade-offs within a global supply network.
Problem
How resilient is a sustainability-driven supply chain when multiple tiers depend on concentrated sourcing and long-haul logistics?
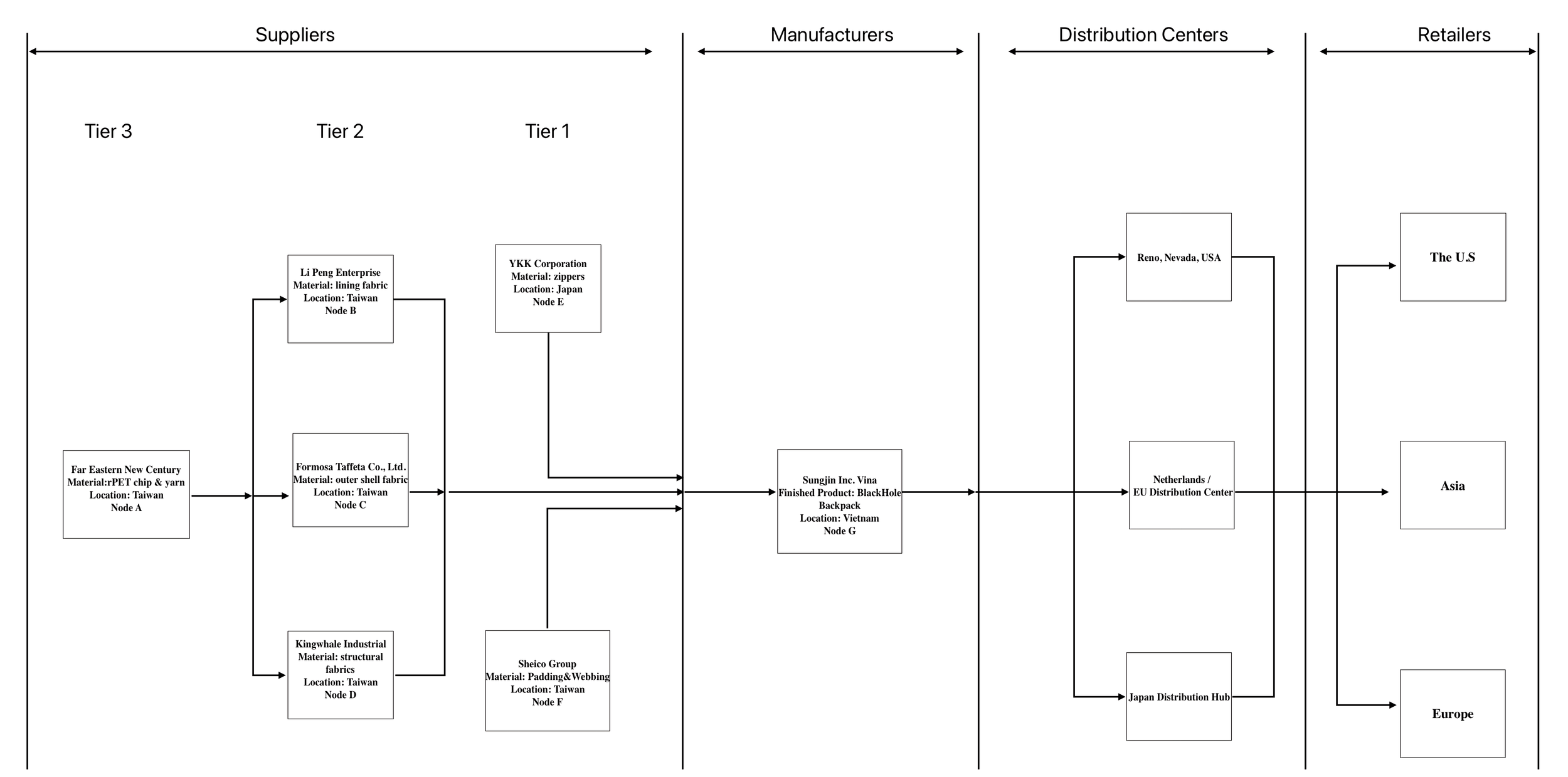
Supply Chain Structure
Analytical Focus
Supplier and geographic concentration
Manufacturing and logistics dependency
System-level risk amplification
Operational constraints introduced by sustainability standards
Key Insights
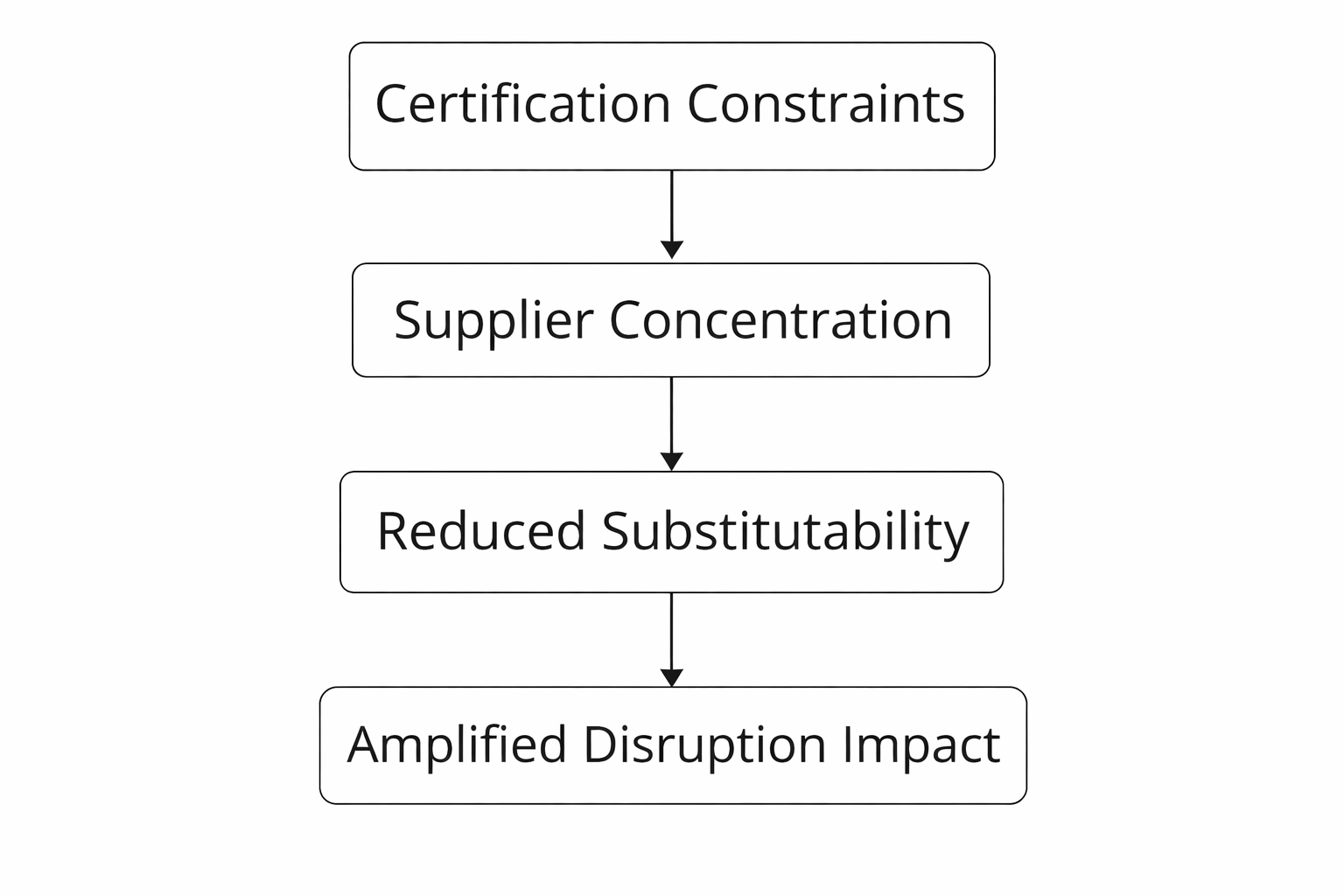
Risk Amplification Mechanism
Supplier and geographic concentration amplify systemic risk
When multiple supply chain tiers rely on a narrow set of certified suppliers within the same region, disruptions propagate quickly across the entire system.Sustainability constraints reduce substitutability under disruption
Environmental certification requirements and ethical sourcing standards limit the ability to switch suppliers or logistics modes in response to shocks.Long-haul logistics magnify disruption impact
An emissions-driven reliance on ocean freight increases exposure to port congestion, climate events, and global shipping volatility, extending recovery time after disruptions.
Strategic Takeaways
Resilience must be designed alongside sustainability goals
Sustainability improves long-term performance only when resilience and flexibility are explicitly incorporated into supply chain design.Diversification is effective only when constraints are addressed
Supplier and manufacturing diversification require parallel expansion of certified capacity; otherwise, concentration risk persists despite geographic spread.Proactive risk monitoring is a strategic necessity
Early detection of geopolitical, climate, and logistics risks enables faster response in tightly constrained supply chains.